The Radical Change of the “Network Topology”
When we think about the radical change that industry is facing in the production, we usually focus on the realization of a factory automation as much as possible oriented to the “incipt” of the fourth industrial revolution (Industry 4.0). This translates into the realization or transformation of physical production system into an operating environment with totally different capabilities than in the past, necessary for survival in the increasingly competitive and lean globalized market, efficient in the purpose of economic sustainability of the company, resources, environment, and ready for interoperability in communications with other systems and the outside world.
The digital transformation of the industrial world, of its production machines, of automation systems, are forcing an increasing evolution also of sensors as primary source and origin of data. New technologies, and related physics principles, are taking over in the generation of a new range of sensors, while the current ones are evolving towards an increasing digitalization, functional intelligence, programmability and flexibility of use.
The main function of sensing or measurement is characterized by the addition of secondary functions such as integrated diagnostics, condition monitoring and digital connectivity: in short, towards the real definition of IIoT component. Therefore, having highly technological I/O evolved towards I4.0 paradigms, has also involved a radical revision of the topological infrastructure of the network of I/O devices and control systems in the machine or in the Automation system.

Towards a single digital communication layer
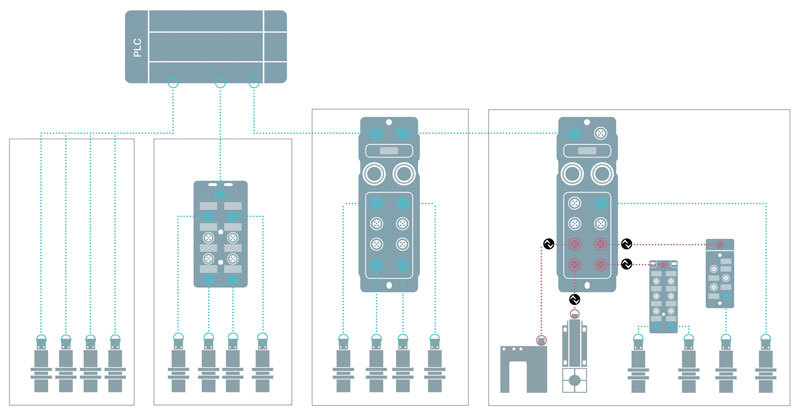
The old structure characterized in the standard by a PLC, to which I/Os (sensors and actuators) are connected through their hardware board, is no longer adequate or optimized to support new hardware architectures and digital communications between devices. The pyramid model of factory architecture is evolving towards a single digital communication layer with Ethernet-based preferred fieldbus, following the philosophy of IIoT/IoT objects interconnected in a network of relationships in which end products and digital modeling of business processes can also participate.
It all boils down to the following core requirements, summarized as a reminder for all companies that are implementing these transformations, and perfectly aligned with a vision pursued globally with aligned activities to solve each topic:
– Digitalization – creation of digital systems
– Communication – digital and two-way communication between systems
– Ethernet Connectivity – as a basic protocol for connecting systems at every level and to the web
– IoT and IIoT – creation of objects with autonomous, cognitive intelligence and interconnection
– AI – Artificial Intelligence, Machine/Deep Learning, Neural Networks
– Networking – structured automation, modular, programmable, intelligent in I/O management
– Artificial Vision – control actions and analysis of high complexity and mixed objects
– Robotics – collaborative or cognitive robotics
– Identification & Traceability – RFID, information link between products and systems, warehouse, supply chain, distribution, services.
But considering only the transformation of your industrial automation is not enough: a broader vision is needed that must answer the classic questions “why, what and how” will this bring results to my company?”.
Why?
“Because everyone does it” is not an answer. “To take advantage of the tax breaks and incentives provided by the state”: ok, but only with the perceived and understood goal of a consequent business transformation that is maintained in the prepositional and advantageous purposes for the future as well. “So as not to be left behind or cut off” is only a necessity and consequence (also forced by globalization). We need to deeply understand the needs of this digital transformation. On the one hand, the re-design of one’s own factory must correspond to a transformation or integration of high-tech production machines and systems, which have the ability to communicate digitally and intelligently with each other and the outside world.
On the other hand, the transformation must also include the processes of production and logistics that must be integrated to take advantage of the new production infrastructure created, mixing with digital-twin models of complementary processes (e.g. design, marketing, MES, …) for maximum benefits and objectives of efficiency and adaptation to market needs and availability/management of resources.
What?
What results must it bring? The creation of the “Smart Factory” and “Smart Manufacturing”. In other words, a model of smart and cognitive factory, which manages to produce in the best way and with maximum efficiency, on the real needs and demands of the market in a lean & on-demand way, adapting to external variables (conveyed on the web), receiving feedbacks also from its own products increasingly IoT objects, using and recycling local and planetary resources, focused on sustainability.
The creation of new business models focused on servitization, i.e. the possibility of creating added services on products for the benefit of the parties (producer/consumer) and the supply-chain.
How?
How and what should I add and do in this transformation? This is all fine and probably effective in the near future, but it needs to be transformed step by step, gradually determining objectives and goals commensurate with one’s own production reality in terms of economic sustainability and capacity/speed of development and integration. The benefits will certainly be amplified and more visible when everyone has adapted to this Industrial Revolution 4.0. In short, as a result, the sale of a good product or service at contained and optimized costs of development, realization and distribution, perfectly in tune with the request, sustainable in terms of resources, use and recycling, when possible smart and source of further information for the continuous improvement of everything, without neglecting the social aspects and added welfare that could be achieved to sustain a planet in demographic growth and badly exploited by human beings.